Understanding The Sustainable Food Packaging Revolution
The food packaging industry is experiencing a major shift. Driven by consumer demand, government regulations, and growing environmental awareness, the industry is rapidly adopting sustainable food packaging. This isn’t a passing fad; it’s a complete change in how we protect and deliver food, impacting everything from materials and manufacturing to marketing and consumer habits.
Drivers of Change
Consumer preferences are a major force behind this shift. Increasingly, consumers are choosing products with sustainable packaging, showing they prioritize environmental responsibility. Governments worldwide are also implementing stricter regulations on packaging waste, including bans on single-use plastics and extended producer responsibility programs. These regulations encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices. These combined pressures are a strong incentive for innovation and investment in sustainable alternatives.
The Economic Impact
This movement isn’t just about ethics; it’s a significant economic opportunity. The sustainable packaging market, including food packaging, has grown substantially. By 2023, it was valued at $276 billion, and projections show it more than doubling to $558 billion by 2034. This growth demonstrates the increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions and the potential for businesses to prosper. Companies investing in sustainable food packaging are not only helping the planet but also positioning themselves for long-term financial success.
Rethinking Traditional Materials
Traditional materials like plastic and Styrofoam are facing competition from innovative alternatives. These include renewable resources, like plant-based plastics, along with biodegradable and compostable options. Some companies are using materials like mushroom roots or seaweed for packaging, which offer unique benefits and reduced environmental impact. This shift requires reassessing the entire supply chain, from raw materials to disposal.
Challenges and Opportunities
The move to sustainable food packaging comes with both challenges and opportunities. Companies face difficulties sourcing sustainable materials at scale, adapting manufacturing processes, and managing costs. However, these challenges create openings for innovation, brand differentiation, and a stronger brand reputation. Businesses embracing sustainability can attract environmentally conscious customers, comply with regulations, and contribute to a circular economy. This revolution requires a comprehensive approach, considering the entire lifecycle of a product and its packaging.
Market Growth That Actually Matters
Consumer demand for eco-conscious products is steadily rising. This isn’t a fleeting trend; it’s driving significant growth in the sustainable food packaging market. For businesses ready to adapt and innovate, this presents a major opportunity. However, this growth isn’t universal, and understanding the market dynamics is essential for success.
Regional Growth and Investment
Sustainable food packaging adoption varies across regions. Europe, with its strict regulations and environmentally aware consumers, has quickly embraced these changes. Other regions are catching up, influenced by both consumer preferences and evolving regulations. This creates a diverse market landscape with opportunities for both early entry in some markets and long-term potential in others. Growing investment in sustainable packaging solutions reflects this market’s long-term viability.
E-Commerce and Lifestyle Changes
The growth of e-commerce has significantly impacted food packaging needs. The demand for protective and efficient shipping materials has fueled the search for sustainable alternatives. Changing consumer lifestyles, like the increasing demand for convenient foods and on-the-go meals, present new challenges and opportunities. Think single-serve portions, resealable packaging, and materials suitable for both hot and cold items. These factors contribute to the expanding market and the growing variety within sustainable food packaging. The real estate industry is also joining the movement, increasingly focusing on sustainability.
Regulatory Pressures and Market Dynamics
Government regulations heavily influence the sustainable food packaging market. Bans on single-use plastics, extended producer responsibility schemes, and labeling requirements encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices. This regulatory environment is complex and constantly evolving, requiring businesses to stay informed and adapt. These regulations also create a level playing field and encourage innovation. The food packaging market is predicted to grow steadily, reaching a projected value of $661,200 million by 2035, up from $391,500 million in 2025, with a CAGR of 5.3%.
Cost Considerations and Supply Chain Impacts
Sustainable packaging often involves higher initial costs compared to traditional options. However, considering the total lifecycle cost, including disposal fees and potential environmental penalties, sustainable choices can offer long-term savings. Adopting sustainable practices can enhance a company’s brand image and attract environmentally conscious consumers, boosting sales and loyalty.
Managing supply chains for sustainable materials can be complex. Sourcing enough high-quality, sustainably sourced materials requires careful planning and supplier collaboration. This highlights the need for strong supplier relationships and long-term partnerships.
Market Adoption Timelines
Sustainable food packaging adoption varies across product categories. Ready-to-eat meals and snacks, for instance, have seen rapid adoption due to consumer demand and the availability of eco-friendly materials. Other categories, like beverages, may face challenges with material performance and shelf life, leading to slower adoption. Understanding these nuances is crucial for businesses crafting sustainable packaging strategies. Realistic adoption timelines should account for material availability, technological advancements, and consumer preferences.
What Consumers Really Want (And Actually Buy)
Market growth is important, but understanding consumer behavior is just as crucial. Often, there’s a disconnect between what consumers say they want and their actual purchases. This section explores the psychology behind consumer choices, focusing on how brands can close this gap with sustainable food packaging.
The Intention-Action Gap
Consumers are increasingly aware of environmental problems and often express a preference for eco-friendly products. However, this doesn’t always translate into sales.
Practical factors like price, convenience, and perceived product quality can sway buying decisions. This creates the intention-action gap, a real challenge for brands trying to promote sustainability.
Overcoming this gap requires understanding the psychology of consumer choices and adapting marketing strategies accordingly. Highlighting benefits beyond environmental impact, like product freshness or convenience, can influence purchases.
How Brands Build Loyalty Through Sustainable Packaging
Smart brands are using sustainable packaging to build customer loyalty. This goes beyond using recycled materials.
It involves clear communication about the brand’s sustainability initiatives, emphasizing the positive impact of these choices. This builds a sense of shared values with customers, creating a strong connection.
Also, offering innovative and convenient packaging solutions like reusable containers or compostable materials enhances the customer experience and boosts the brand’s image. Transparency is vital: clearly explaining the materials used and their environmental benefits builds trust.
Messaging That Resonates (And Messaging That Doesn’t)
Effective communication is key to promoting sustainable food packaging. Focusing on real benefits, such as reduced plastic waste or the use of renewable resources, is more effective than abstract ideas.
For example, stating that packaging is made from 100% recycled materials is more powerful than vaguely mentioning “eco-friendliness.” Avoiding greenwashing, or misleading environmental claims, is crucial. Consumers are getting smarter and can spot inauthenticity, which can hurt a brand’s reputation.
A recent consumer report revealed that 54% of respondents specifically chose products with sustainable packaging in the past six months. This shows a major shift towards eco-conscious consumerism. Explore this topic further.
Transparency, Education, and Authentic Communication
Transparency, education, and authentic communication are becoming powerful tools in the sustainable food packaging market. Brands that openly share their sustainability efforts, including both struggles and wins, build stronger customer relationships.
Educating consumers about the benefits of sustainable packaging and proper disposal methods allows them to make informed decisions. Authenticity is paramount; customers can tell the difference between genuine commitment and marketing ploys.
Brands must align actions with words, demonstrating a true commitment to sustainability in all aspects of their business. This builds trust and encourages long-term loyalty, fostering relationships built on shared values.
Materials That Work In The Real World
Choosing the right sustainable food packaging means understanding the pros and cons of different materials. It’s not just about being eco-friendly; it’s about protecting food, following regulations, and meeting business goals.
Plant-Based Plastics: A Promising Alternative
Plant-based plastics, made from sources like corn or sugarcane, offer a renewable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. These materials often have a smaller carbon footprint and can be compostable in the right environment.
However, their performance can vary. Some are less durable or heat-resistant than conventional plastics. This makes them suitable for some applications, like dry goods or short shelf-life products, but not for others.
Bio-Materials: Innovation From Nature
Innovative bio-materials from sources like seaweed or mushroom roots are gaining popularity. These materials are often compostable and biodegradable, offering exciting ways to reduce packaging waste.
However, cost and scalability remain obstacles, limiting widespread use. For example, mushroom packaging, while promising, is currently more expensive than conventional options. This makes it better for niche markets than mass production.
Edible Packaging: A Delicious Solution?
Edible packaging, a fascinating concept, faces practical challenges. While some edible films and coatings exist, fully edible containers that meet food safety and preservation standards are still difficult to create.
However, this field has great potential for reducing waste and creating unique consumer experiences. Imagine eating a yogurt cup or a candy wrapper! While not yet mainstream, edible packaging offers a glimpse into the future of sustainable solutions.
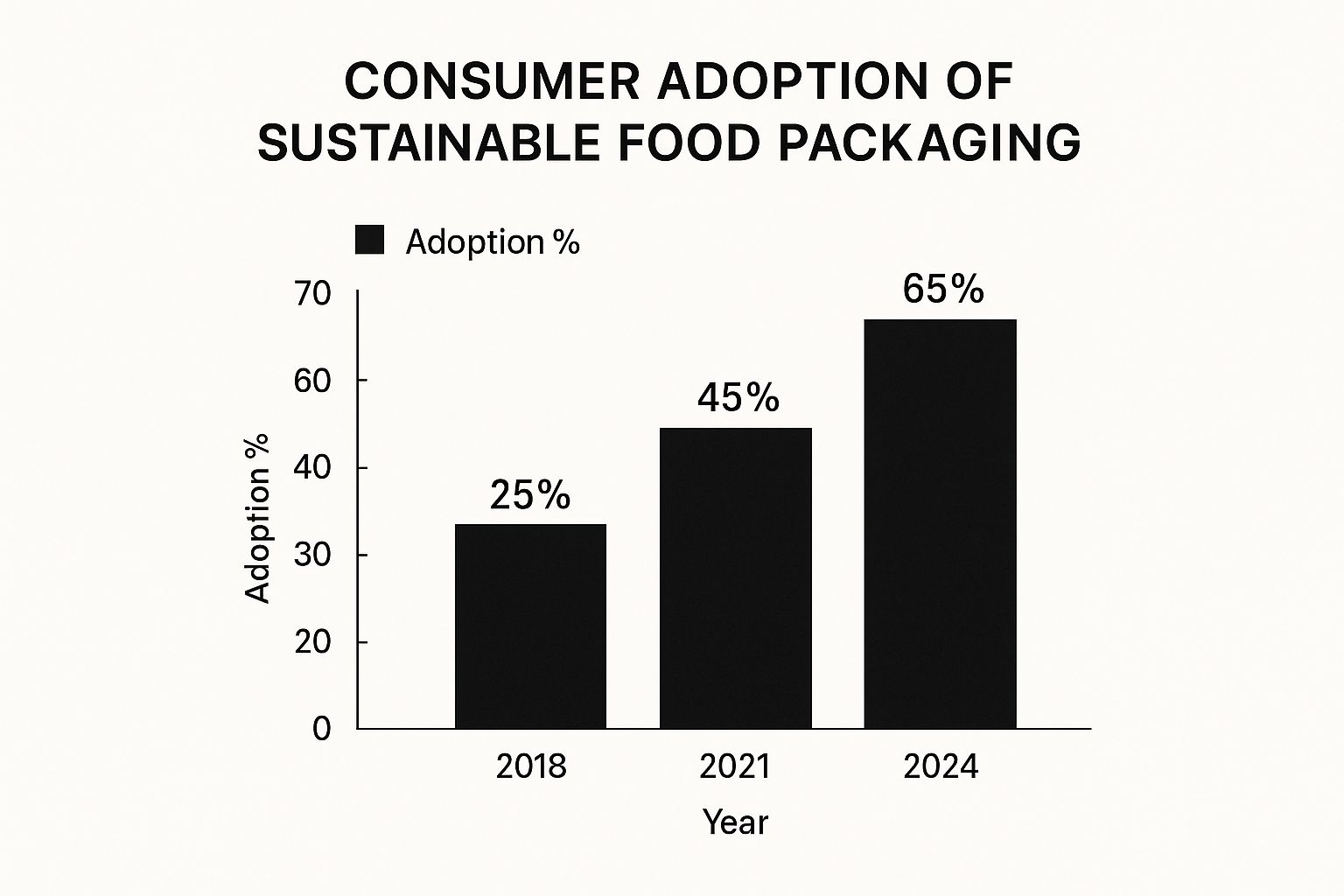
The infographic above shows growing consumer interest in sustainable food packaging. From 25% adoption in 2018, it rose to 45% in 2021 and is projected to reach 65% by 2024. This clearly demonstrates increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly packaging.
Balancing Functionality and Sustainability
Choosing sustainable materials involves compromises. Biodegradable packaging might be great for the environment, but it might not provide the necessary shelf life for all products. Similarly, compostable materials need specific composting conditions, not always available to consumers.
This means carefully balancing material properties with product needs and disposal options. Companies with comprehensive sustainable packaging strategies achieve 67% better brand perception and 23% higher customer retention compared to those using conventional packaging.
To help understand the various materials and their applications, the table below provides a comparison guide:
Sustainable Food Packaging Materials Performance Guide
| Material Type | Environmental Impact | Cost Level | Durability | Best Applications | Decomposition Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-based Plastics (PLA) | Lower carbon footprint than traditional plastic | Moderate | Varies, generally lower than traditional plastic | Dry goods, short shelf-life products, films | 6 months – 2 years (in industrial composting facilities) |
| Mushroom Packaging | Compostable and biodegradable | High | Moderate | Protective packaging, niche products | A few weeks |
| Seaweed Packaging | Compostable and biodegradable | High | Moderate | Films, coatings | A few weeks |
| Edible Films/Coatings | Minimal waste | Moderate to High | Low | Candy wrappers, edible coatings | A few days |
This table highlights the varying costs and durability among sustainable materials, as well as their environmental benefits. While some, like mushroom and seaweed packaging, offer excellent biodegradability, they are more expensive. Plant-based plastics provide a more cost-effective option, but with trade-offs in durability and heat resistance.
Emerging Innovations: What’s Next?
The future of sustainable food packaging is full of exciting possibilities. Researchers are exploring materials from agricultural waste, developing bioplastics with improved performance, and investigating new recycling technologies.
These advancements aim to solve current limitations and create truly circular packaging systems. Packaging waste becomes a resource, returning to the production cycle instead of ending up in landfills or the ocean. From new materials to innovative manufacturing, the future of sustainable packaging is dynamic and full of promise.
Implementation Strategies That Actually Work
Transitioning to sustainable food packaging requires a well-defined strategy and efficient execution. This section offers practical guidance based on companies that have successfully made this change.
Conducting a Meaningful Packaging Audit
Understanding your current packaging footprint is the first step. A packaging audit analyzes every material used, from the primary container to the shipping box. This helps identify areas for improvement and measure the environmental impact of current practices. Are you using excessive plastic? Are there opportunities to use recycled content? This assessment sets the foundation for realistic sustainability goals.
Setting Realistic Goals and Timelines
Achievable goals are essential. Focus on incremental changes instead of a complete overhaul. For example, begin by replacing one high-volume item with a sustainable alternative. This allows you to test and refine your approach before scaling up. Establish realistic timelines, acknowledging that sourcing new materials and adapting processes takes time.
Supplier Selection and Management
Choosing the right suppliers is crucial. Look for partners dedicated to environmental responsibility and transparency. Do they offer certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification for paper products or recycled content certifications for plastics? Effective communication and collaboration with suppliers are essential throughout the transition.
Balancing Environmental Objectives with Business Requirements
Sustainability shouldn’t compromise product protection or affordability. Balancing environmental goals and business needs is critical. Consider factors like product shelf life, transportation requirements, and cost constraints. A biodegradable material might be ideal environmentally, but unsuitable for products requiring a long shelf life.
Measuring Success and Demonstrating ROI
Tracking progress and demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of sustainable packaging is crucial for stakeholder support. Measure metrics like waste reduction, material usage, and transportation costs. For example, calculate the plastic waste reduction from switching to a plant-based alternative. This data showcases your environmental impact and highlights the financial benefits of sustainability.
Case Studies and Lessons Learned
Learning from others’ experiences can save time and resources. Analyzing case studies of successful (and unsuccessful) sustainable packaging implementations provides valuable insights. What challenges did companies face, and how did they overcome them? Some companies have struggled with the higher initial costs of sustainable materials but discovered long-term savings through reduced waste disposal fees.
Building Stakeholder Support
Implementing sustainable packaging requires buy-in from everyone involved, including employees, customers, and investors. Communicate your sustainability goals clearly and transparently. Emphasize the environmental and economic advantages of your initiatives. This creates a shared understanding and fosters support for your efforts, ensuring the long-term success of your sustainable packaging program.
Navigating The Regulatory Maze
The regulatory landscape for sustainable food packaging is complex and ever-changing. However, understanding it can provide a real competitive edge. Staying informed about current and upcoming regulations is essential for businesses in the food industry. This section breaks down the key regulatory areas, focusing on how to transform these challenges into opportunities.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws hold producers responsible for the end-of-life management of their packaging. This shifts the responsibility of recycling and waste management from municipalities to the companies that create the packaging. EPR programs differ by region, encompassing different materials and collection systems.
Some programs concentrate on specific materials, like plastics, while others are broader. Understanding the specific requirements of each program is critical for compliance.
Single-Use Plastic Bans
Many regions are implementing single-use plastic bans, targeting items like straws, cutlery, and bags. The aim is to reduce plastic waste and promote the use of sustainable alternatives. For example, some cities have completely banned plastic shopping bags, which has boosted the demand for paper or reusable bags. This shift creates opportunities for businesses offering sustainable replacements.
Regional Approaches to Packaging Regulation
Different regions are adopting diverse approaches to packaging regulation. The European Union, for instance, has stringent regulations on packaging waste and recycling targets. Other areas are implementing labeling requirements that identify the material composition and recyclability of packaging.
This means businesses must tailor their packaging strategies according to the specific regulations in their target markets. Staying informed about these varying regulations helps avoid penalties and ensures continued market access.
Proactive Compliance Strategies
Successfully navigating the regulatory landscape demands a proactive approach. This goes beyond simply meeting the minimum requirements and involves actively seeking opportunities to exceed them. Regular packaging audits can identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Investing in sustainable packaging materials and technologies demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility. This positions businesses as leaders in the market.
Certification Requirements and Voluntary Standards
Numerous certifications and voluntary standards exist for sustainable packaging, such as Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification for paper and recycled content certifications for plastics. While some certifications are mandatory in certain regions, others are voluntary.
Achieving these certifications showcases a commitment to sustainability and can boost a brand’s reputation. This can be a powerful marketing asset, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Understanding the specific requirements of relevant certifications helps businesses choose the most suitable options for their products and target markets.
Turning Regulatory Challenges into Market Opportunities
Regulatory changes, while potentially challenging, can create significant market opportunities. Businesses that proactively adapt to new regulations and invest in sustainable packaging solutions can gain a competitive advantage. This means viewing regulations not as obstacles, but as catalysts for innovation and market differentiation.
By adopting sustainable practices, businesses can strengthen their brand image, attract new customers, and contribute to a more sustainable future. This approach transforms regulatory compliance into a strategic advantage.
Future Innovations Worth Watching
The world of sustainable food packaging is constantly changing. To stay competitive, businesses need to be aware of new trends and technologies. This proactive approach allows them to adapt, seize opportunities, and establish themselves as leaders in sustainability. When considering future innovations, the impact of packaging waste on our oceans is paramount.
Smart Packaging: The Next Level of Interaction
Smart packaging does more than just hold food; it interacts with both the product and the consumer. Think of packaging that changes color to indicate spoilage, or sensors that monitor freshness in real time. This technology empowers consumers to make informed choices, minimizes food waste, and improves food safety. The result is greater convenience, healthier consumption, and a reduced environmental impact.
Nanotechnology: Tiny Particles, Big Impact
Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials at the atomic level. In food packaging, this translates to creating materials with enhanced properties, like better barrier protection and increased strength. Picture a thinner plastic film that offers the same strength as traditional packaging, reducing both material usage and waste. Nanotechnology also shows promise for developing antimicrobial coatings that extend shelf life and lessen the need for preservatives.
AI-Optimized Design: Smarter, More Efficient Packaging
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping packaging design. Artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze large datasets to optimize packaging shapes, sizes, and materials. This results in more efficient designs that use less material, lower transportation costs, and decrease waste. This increased efficiency benefits both the environment and a company’s bottom line.
Emerging Collaborations: Power in Partnerships
Collaboration is essential for advancing sustainable food packaging innovation. Partnerships between food producers, technology companies, and material scientists are unlocking exciting new possibilities. These collaborations bring together expertise from different areas, speeding up the development and use of new materials and technologies. This joint effort is crucial for overcoming challenges and creating significant industry change.
Investment Trends and Promising Startups
Monitoring investment trends offers valuable insights into which technologies are gaining traction. Many promising startups are developing innovative solutions in areas like biodegradable materials, compostable packaging, and smart packaging technologies. Keeping tabs on these up-and-coming companies provides key information about the future of the industry. This awareness helps businesses make strategic decisions about investment and technology adoption.
Breakthrough Technologies: What’s on the Horizon?
Several exciting technologies are approaching commercial viability. These include:
- Bioplastics from agricultural waste: This involves transforming discarded crop remnants, like corn stalks or wheat straw, into durable, eco-friendly packaging. This process reduces reliance on fossil fuels and creates valuable uses for agricultural byproducts.
- Edible films and coatings: While still in the early stages of development, these innovations have the potential to eliminate packaging waste for specific products.
- Advanced recycling technologies: These new techniques enable the recycling of materials that were previously difficult or impossible to process, fostering more closed-loop systems.
Commercial Viability and Integration Strategies
Understanding realistic timelines for commercial viability is vital for businesses developing their packaging strategies. Some technologies are ready for immediate use, while others may be years away from widespread adoption. Assessing these timelines allows companies to make informed decisions and smoothly incorporate new solutions into their operations.
The following table provides a possible timeline for some of these advancements:
Emerging Sustainable Packaging Technologies Timeline
| Technology | Current Status | Expected Commercial Launch | Potential Impact | Key Players |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Packaging (Sensors, Indicators) | Early Adoption | Next 2-5 years | Reduced food waste, enhanced safety | Various tech startups and packaging companies |
| AI-Optimized Design | Emerging | Next 5-10 years | Improved efficiency, reduced material usage | Software companies, packaging design firms |
| Bioplastics from Agricultural Waste | Pilot Projects | Next 5-10 years | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels | Biomaterial companies, agricultural businesses |
| Edible Films/Coatings | Research & Development | 10+ years | Elimination of packaging waste | Food science research institutions, startups |
This table shows the different development stages of these technologies. It demonstrates that while some, like smart packaging, are nearing broader use, others, such as edible films, still require further research.
MrTakeOutBags.com is dedicated to offering sustainable packaging solutions. Discover our wide selection of eco-friendly options for your business. We offer a variety of products, including compostable containers, recycled paper bags, and plant-based plastics, designed to help you achieve your sustainability goals and satisfy your customers.







Comments are closed.