Understanding What Makes Packaging Truly Food Safe
When it comes to food, safety is undeniably important. Packaging acts as a crucial shield against contamination and spoilage. Food safe packaging isn’t just about containing the food; it’s about actively preserving its quality and ensuring it remains safe for consumption. This exploration delves into the key elements that set effective food safe packaging apart.
Key Properties of Food Safe Packaging
Effective food safe packaging hinges on a few vital properties. The packaging material needs to be non-reactive, meaning it won’t interact chemically with the food inside. This prevents harmful substances from leaching into the food, maintaining its flavor and safety. The packaging also needs to act as a robust barrier against external threats like bacteria, moisture, and oxygen. This barrier helps maintain quality and extends the product’s shelf life.
- Barrier Protection: Shields the food from moisture, oxygen, and microorganisms.
- Non-Reactivity: Guarantees the packaging doesn’t contaminate the food with chemicals.
- Durability: Ensures the packaging remains intact throughout handling and transport.
- Preservation: Maintains product freshness and extends its shelf life.
The Role of Material Selection
The material you choose significantly impacts the safety and effectiveness of food packaging. Common materials include various types of plastics, glass, metal, and paper. Each material has specific properties that make it suitable for particular uses.
For example, glass is inert and offers an excellent barrier against oxygen, which makes it perfect for sensitive products. Its fragility, however, can be a concern. Plastics are versatile, providing a wide array of barrier properties, but must be carefully chosen to ensure they are food-grade and meet safety standards.
Beyond the Material: Design and Manufacturing Processes
The design and manufacturing of food safe packaging are just as important as the materials themselves. Secure sealing and closure mechanisms are vital to prevent leaks and maintain a strong barrier. Manufacturing must follow strict hygiene standards to minimize contamination risks during production. Even the adhesives used must be food-safe and comply with regulations to avoid chemical migration into the food. Understanding these aspects allows businesses to choose packaging wisely, protecting both their products and customers.
How Food Safe Packaging Evolved Into Big Business
The journey of food safe packaging, from simple storage solutions to a massive industry, is a compelling story of consumer needs meeting technological innovation. Initially, preserving food relied on methods like salting, smoking, and pickling. But as societies became more complex and supply chains stretched further, the demand for stronger and more adaptable packaging grew. This demand fueled the development of new packaging materials and techniques.
From Preservation to Protection: A Shift in Focus
Early food packaging primarily focused on extending shelf life. Over time, however, the focus shifted to preventing contamination and guaranteeing food safety. Growing consumer awareness of foodborne illnesses and their health risks spurred this change. Furthermore, regulations from agencies like the FDA played a key role in shaping industry standards.
The Rise of Specialized Materials and Technology
Modern food safe packaging is defined by the use of specialized materials approved for direct food contact. These materials are rigorously tested to ensure they don’t release harmful substances into food. For instance, specific types of plastics, glass, and metal are now widely used because of their barrier properties and non-reactive nature.
The development of these materials has gone hand-in-hand with advancements in manufacturing, enabling greater precision and control over packaging production. This progress has been crucial in minimizing contamination risks and improving the overall safety of our food supply.
Historically, food-safe packaging has come a long way, evolving with technology and regulations to address contamination risks and foodborne illnesses. Modern times have seen a significant rise in the use of materials certified for food contact, influenced by strict global safety regulations. In 2024, the global food packaging market was valued at approximately USD 458.6 billion, and it’s projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% between 2025 and 2034, demonstrating continued investment in safer packaging solutions.
Consumer Demand as a Driving Force
Consumer demand for safer and more convenient food options has further boosted the food safe packaging industry. This has led to features like tamper-evident seals and resealable packaging, which increase consumer confidence and minimize food waste.
As consumers become more selective about the products they buy, businesses are increasingly investing in packaging that not only protects food but also conveys quality and fosters brand trust. This consumer-centric approach ensures ongoing growth and innovation within the industry.
Market Growth Reveals Massive Opportunities Ahead
The food safe packaging sector isn’t just about keeping products safe; it’s a vibrant market that’s rapidly expanding. This growth creates exciting opportunities for businesses that understand what’s driving this increasing demand. Let’s delve into the factors contributing to this market expansion and the potential it holds.
Understanding the Drivers of Growth
Several key factors fuel the growth of the food safe packaging market. A major influence is the rising consumer awareness of food safety and quality. People are increasingly concerned about what they eat and how it’s packaged.
Additionally, growing urbanization and shifting lifestyle preferences influence the packaging that consumers seek. The demand for convenient, on-the-go meals, for example, requires packaging that maintains both safety and portability.
Furthermore, stricter regulations and quality standards set by governments worldwide accelerate the adoption of food safe packaging. These regulations ensure that businesses prioritize consumer safety and product integrity, contributing to overall market growth. Companies investing in robust food safe packaging solutions are not only meeting these requirements but also responding to evolving consumer expectations.
The global food packaging market has seen remarkable growth, reflecting the increasing demand for safe and sustainable packaging. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately USD 398.5 billion. It’s projected to reach around USD 421.6 billion in 2025.
Forecasts predict a steady Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of about 6.06% between 2025 and 2034. By 2034, the market is expected to reach an estimated USD 718.29 billion.
Regional Variations and Opportunities
Growth in the food safe packaging market varies across different regions. Developing economies, with their growing populations and rising disposable incomes, often experience faster growth.
However, developed regions also offer substantial opportunities, driven by consumer demand for premium, sustainably packaged products. This creates a diverse landscape of opportunities for businesses, requiring strategic approaches tailored to specific regional needs and preferences.
Investment and Innovation
The food safe packaging industry is seeing significant investment in research and development. This focus on innovation leads to new materials and technologies that enhance safety, extend shelf life, and improve the consumer experience.
For example, advancements in antimicrobial packaging and modified atmosphere packaging are changing how food is protected and preserved. These ongoing investments ensure that food safe packaging continues to evolve, meeting the changing demands of both the food industry and consumers.
Choosing Materials That Actually Protect and Preserve
Beyond simply complying with regulations, selecting the right materials is critical for exceptional food protection. This means understanding the properties that define truly food-grade materials and how they prevent chemical migration while maintaining product integrity. It’s all about how the packaging interacts with the food inside.
Material Selection: A Balancing Act
Choosing the right material involves balancing protection with preservation. Food-safe packaging must act as a barrier against external contaminants like bacteria, moisture, and oxygen. A material might excel at blocking moisture but allow oxygen to permeate, leading to spoilage. The packaging also shouldn’t chemically interact with the food, altering its flavor or introducing harmful substances.
- Barrier Properties: Keeping contaminants out and freshness in.
- Chemical Inertness: Ensuring the packaging doesn’t react with the food.
- Strength and Durability: Holding up during handling and transportation.
Eco-Friendly Options: Sustainability Meets Safety
Leading brands are increasingly prioritizing both safety and environmental responsibility. They are achieving this balance through the use of innovative biodegradable and recyclable materials. This shift is driven by growing consumer demand for sustainable choices and increasing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional packaging.
Eco-friendly, food-grade options are now essential. The market for these materials is expanding rapidly due to consumer demand for health-conscious and environmentally sustainable products. The eco-friendly food packaging sector is expected to nearly double, from USD 211.66 billion in 2025 to USD 392.37 billion by 2034.
Evaluating Material Performance
Selecting effective food-safe packaging requires careful evaluation. Understanding certification requirements, such as those from the FDA, is crucial for ensuring compliance with safety standards and building consumer trust.
| Feature | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Barrier Properties | Oxygen transmission rate, moisture vapor transmission rate |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistance to oils, acids, and other food components |
| Temperature Tolerance | Ability to withstand temperature changes during storage and transport |
| Durability | Resistance to punctures, tears, and other damage |
Consider the specific needs of the food product. Oily foods, for instance, require packaging with high grease resistance. This targeted approach helps ensure the chosen material effectively protects and preserves the food from production to consumption.
Navigating Compliance Without Getting Lost In Red Tape
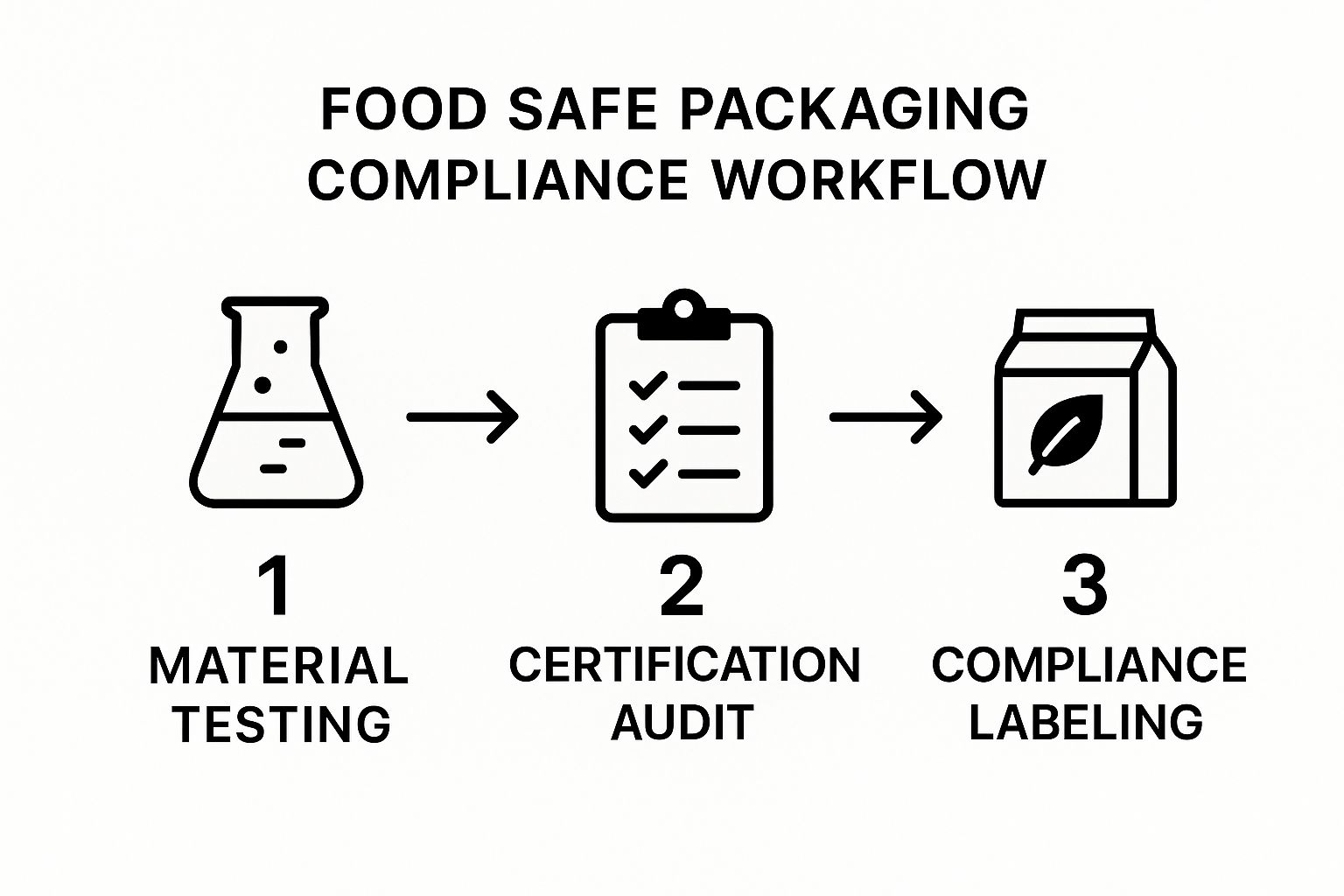
This infographic illustrates the three core steps for food safe packaging compliance: material testing, a certification audit, and compliant labeling. These stages ensure your packaging meets the necessary standards. By following this process, businesses build consumer trust and minimize risks.
Food safe packaging regulations can feel overwhelming. However, understanding key requirements simplifies the process. This section breaks down essential regulations from authorities like the FDA and EFSA, offering practical steps to protect consumers and your business.
Understanding Key Regulations
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States and the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) in Europe set the standards for food safe packaging. These regulations cover permitted materials, required testing, and necessary documentation. Choosing the right containers is critical. For example, consider exploring options like eco-friendly food storage containers. Ultimately, proper container selection prevents material contamination and ensures product protection throughout the supply chain.
To help clarify the varying regulations, the table below compares key international regulatory bodies and their specific standards:
Key Regulatory Bodies And Their Food Packaging Standards
| Regulatory Body | Region | Key Standards | Testing Requirements | Approval Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) | United States | 21 CFR, food contact substances | Migration testing, toxicity studies | Pre-market notification or food contact notification |
| European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) | European Union | Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 | Migration testing, risk assessment | Authorization by EFSA |
| Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) | Australia and New Zealand | Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code | Migration testing, risk assessment | Pre-market approval |
| Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) | Canada | Food and Drugs Act and Regulations | Migration testing, toxicity studies | Pre-market notification or food contact notification |
| Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) | Japan | Food Sanitation Act | Migration testing, toxicity studies | Pre-market notification or food contact notification |
This table highlights the global variations in food packaging standards, emphasizing the importance of understanding specific regional requirements. While migration testing is a common requirement, the specifics vary. Be sure to research the precise regulations for your target market.
Testing and Approval Processes
Material testing verifies that packaging meets safety standards. This often involves analyzing material composition and assessing its potential interaction with food. After testing, a certification audit confirms that manufacturing processes and facilities adhere to regulations. This process validates the overall safety and suitability of the packaging.
Documentation and Quality Assurance
Thorough documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance. This includes records of material testing, audit results, and quality control procedures. Implementing a robust quality assurance system ensures consistent compliance by tracking processes and identifying potential issues early. This proactive approach builds consumer trust and minimizes the risk of costly recalls or legal challenges. For instance, clear standard operating procedures (SOPs) for handling and storage guide employees and promote a strong safety culture.
Cutting-Edge Tech That’s Changing The Game
The future of food-safe packaging has arrived, bringing with it technologies designed to actively protect and monitor food quality. This isn’t just about containing food; it’s about establishing an environment that preserves freshness and prolongs shelf life. These advancements are a direct response to the increasing demand for safer, more transparent, and sustainable packaging.
Intelligent Packaging Systems: The Future of Food Safety
Intelligent packaging systems are a significant step forward. These systems incorporate interactive features that respond to the food and its surrounding environment.
For example, antimicrobial packaging releases substances that combat bacterial growth. This extends shelf life and reduces spoilage, actively working to prevent contamination and ensuring food safety.
Another key development is modified atmosphere packaging (MAP). MAP adjusts the air within the package, decreasing oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide or nitrogen. This slows down the natural decaying process, preserving food quality and freshness.
Real-Time Monitoring With Smart Sensors
Smart sensors are transforming how we track food quality across the supply chain. These tiny devices, embedded within the packaging, deliver real-time data on temperature, humidity, and even the presence of specific gases.
This constant monitoring allows for quick action if conditions deteriorate, minimizing spoilage and waste. It also provides valuable information about product handling and storage, leading to optimized logistics and improved overall efficiency. The result? Food reaches consumers in optimal condition.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Consumers want transparency and security when it comes to their food. Tamper-evident features, such as seals and closures that indicate any attempt at opening, offer assurance that food remains untouched.
Some intelligent packaging systems track a product’s journey from farm to table, creating full supply chain visibility. This builds consumer trust and assists with traceability for product recalls. These packaging advancements align with global efforts to reduce foodborne illnesses, which the WHO estimates cause millions of illnesses and thousands of deaths annually. Stronger packaging safety, combined with regulatory compliance, is critical in minimizing contamination incidents and bolstering consumer confidence. Understanding regulatory compliance in food-safe packaging means knowing the overall landscape.
Barrier Technologies: Protection at a Microscopic Level
Barrier technologies work to prevent external elements from penetrating the packaging. These technologies use microscopic layers within the packaging material to act as selective barriers. They allow certain gases, like carbon dioxide, to pass through while blocking oxygen and moisture, extending shelf life even further.
These precise barrier properties maintain product integrity and freshness without relying heavily on preservatives. This leads to a “cleaner” product, which is attractive to health-conscious consumers.
Your Roadmap To Food Safe Packaging Success
Transforming your food packaging into a safe and efficient system requires a structured approach. This involves careful consideration of material selection, supplier evaluations, and implementing robust quality control processes. These elements work together to ensure a robust and reliable food safe packaging operation.
Material Selection: The Foundation of Safe Packaging
Choosing the right materials is the cornerstone of safe food packaging. This starts with understanding the specific needs of your food products. For instance, oily foods require packaging with high grease resistance, while acidic products may need specialized linings to prevent corrosion and chemical leaching.
- Barrier Properties: Select materials that effectively block oxygen, moisture, and contaminants, acting as a shield for your food.
- Chemical Compatibility: Ensure your chosen material doesn’t react with the food, impacting taste, or introducing harmful substances. Thorough testing is essential.
- Durability and Strength: Packaging must withstand handling and transportation throughout the entire supply chain.
Evaluating Suppliers: A Partnership for Safety
A reliable supplier is essential for food-safe packaging. Look for suppliers who prioritize food safety and have stringent quality control measures in place. Inquire about certifications and testing procedures. A strong supplier partnership ensures consistent material quality and compliance with safety regulations.
To help you choose the right supplier, consider the following:
| Aspect | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Certifications | Look for relevant food safety certifications, demonstrating a commitment to quality. |
| Testing Procedures | Understand how the supplier tests materials to ensure they meet required safety standards. |
| Traceability | Verify the ability to trace materials back to their source, which is critical for product recalls. |
This table summarizes key factors to consider when evaluating potential suppliers. Partnering with a certified and reliable supplier will contribute significantly to your overall food safety efforts.
Implementing Quality Control: Ensuring Consistency
A robust quality control system monitors every stage of the packaging process. Regular inspections, rigorous testing, and meticulous documentation help identify and address potential issues early on. This proactive approach minimizes risks and maintains high quality standards.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine checks of incoming materials, production processes, and finished goods.
- Testing: Perform tests to verify barrier properties, chemical compatibility, and overall packaging integrity.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of quality control procedures, test results, and supplier information.
By adhering to these quality control measures, you can ensure that your packaging consistently meets the required safety standards.
From Planning to Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Transitioning to a food-safe packaging system needs careful planning. Develop a realistic implementation timeline with clearly defined milestones. This roadmap will guide the process and ensure a systematic approach.
The following checklist provides a framework for implementing a food-safe packaging system. It outlines key activities, timelines, metrics, and potential challenges for each phase.
Food Safe Packaging Implementation Checklist
| Implementation Phase | Key Activities | Timeline | Success Metrics | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Evaluate current packaging, identify gaps, and define safety goals. | 1-2 Weeks | Documented gaps and established safety goals. | Resistance to change. |
| Material Selection | Choose materials that meet safety and performance requirements. | 2-4 Weeks | Selected materials meet all requirements. | Sourcing suitable materials. |
| Supplier Evaluation | Select qualified suppliers adhering to food safety standards. | 4-6 Weeks | Approved supplier list. | Finding suppliers meeting all criteria. |
| Implementation | Implement new packaging processes, training, and quality control procedures. | 8-12 Weeks | Successful implementation of new procedures. | Staff training and adoption. |
| Monitoring | Continuously monitor packaging performance, gather data, and adjust. | Ongoing | Consistent positive feedback and test results. | Maintaining consistent monitoring. |
This checklist helps businesses track their progress and identify potential roadblocks. Successfully implementing a food-safe packaging system ultimately protects consumers and enhances brand reputation.
Implementing food safe packaging is an investment that protects your consumers and strengthens your brand. Prioritizing safety and quality builds trust and contributes to long-term business success. Learn more about packaging solutions at MrTakeOutBags.com.






Comments are closed.